VIX and Forex: A Quantitative Look at Global Risk Sentiment
“VIX represents global risk sentiment and uncertainty expectations.” ~ Russell Rhoads
We conducted an in-depth empirical study to examine how the VIX Index—often called the global “fear gauge”—influences major Forex currency pairs. The objective was to identify which currencies behave as risk-on assets and which act as safe-haven (risk-off) assets during periods of heightened market uncertainty.
Data & Methodology
Our dataset consists of:
Daily price data for 25 major Forex pairs
Daily VIX index values
Time period: 2010–2025
To ensure statistical accuracy, we:
Converted all price series into daily log returns
Aligned trading days across Forex and VIX data
Applied Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression for each currency pair
The regression model estimates a beta coefficient for each pair, which measures how sensitive that currency pair is to changes in the VIX.
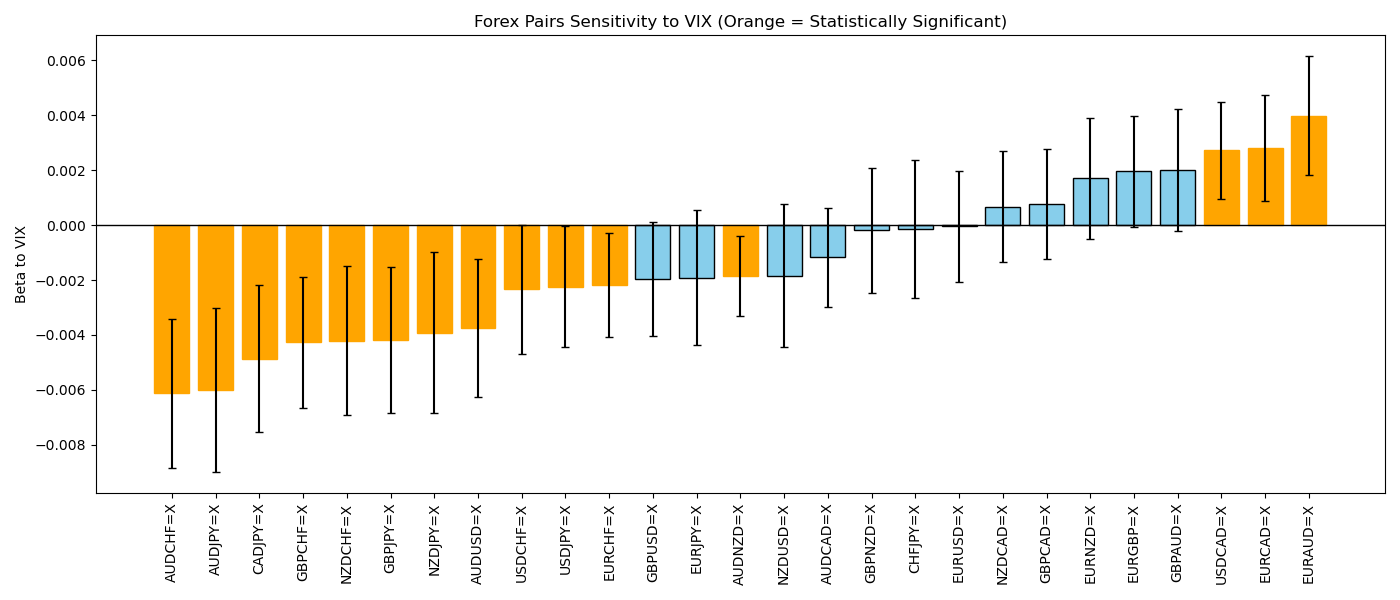
How to Read the Chart
From the visualization:
Blue bars → Overall VIX–Forex correlation
Orange bars → Statistically significant relationships (p < 0.05)
Horizontal zero line → Divides positive and negative sensitivity
Interpretation Rules:
Above 0 (Positive Beta) → Currency pair moves with VIX
→ Indicates risk-off / safe-haven behaviorBelow 0 (Negative Beta) → Currency pair moves against VIX
→ Indicates risk-on / growth-oriented behavior
Findings -
1. Risk-On Currencies (Negative VIX Sensitivity)
Several currency pairs show strong negative beta values, meaning they decline when VIX rises. These are typically:
AUD-based pairs
NZD-based pairs
Emerging or commodity-linked currencies
This confirms that risk-on currencies lose strength during volatility spikes, as investors exit risky assets.
2. Risk-Off / Safe-Haven Currencies (Positive VIX Sensitivity)
On the positive side of the chart, several USD, JPY, and CHF pairs demonstrate positive and statistically significant betas.
This means:
These currencies strengthen when risk rises
They act as safe-haven destinations during fear-driven market conditions
This validates well-known market behavior:
JPY, USD, and CHF gain strength during global stress
Statistical Significance Matters
Only the orange bars represent relationships strong enough to be trusted statistically. This eliminates:
Random correlations
Noise-based market movements
False signals
This makes the model reliable for:
Risk regime classification
Volatility-based trading strategies
Macro sentiment filtering
Trading & Risk Management Implications
This VIX-Forex sensitivity framework allows traders and portfolio managers to:
1. Identify which currency pairs to avoid during volatility spikes
2. Recognize safe-haven flows during global crises
3. Adjust portfolio exposure based on risk sentiment
4. Improve hedging strategies during uncertainty
5. Filter false breakout setups during fear-driven markets
For example:
If VIX is rising rapidly, risk-on pairs like AUD/USD or NZD/JPY become structurally weak.
Meanwhile, USD/CHF or JPY-based pairs gain defensive strength.
This analysis clearly demonstrates that VIX is not just an equity volatility index—it is a global macro risk indicator that directly impacts Forex markets. By statistically quantifying how each currency reacts to fear, traders gain a scientifically grounded tool for understanding market sentiment, capital flows, and volatility regimes.
Instead of reacting emotionally during high-volatility periods, this VIX-Forex sensitivity analysis allows traders to position with logic, probability, and macro alignment.